Long Bone Labeled Epiphysis. Anatomy part i at pope john xxiii high school. Transcribed image text from this question. Compact bone and spongy bone both perform different functions. The model details, with labels, the end regions of a growing long bone, a process called enchondral ossification.
Long bones include the humerus (upper arm), radius (forearm), ulna (forearm) this image represents the parts of a long bone. The labels include proximal epiphysis, proximal metaphysis, diaphysis (bone shaft), distal. The rounded proximal and distal ends of a long bone, which contains mostly spongy bone and develops from secondary ossification centers. The growth plate is located just below the epiphysis and is the portion of the bone in which cartilage proliferates and is mineralized. Long bones have epiphyseal plate, also known by. Within the long bones, the epiphysis is the first to undergo conversion followed by the diaphysis before extending to the metadiaphysis 5,6.

What's the typical gene expression for the epiphysis of human long bones?
File:structure of a long bone.png. · out of many vascular foramina near epiphysis, very few admit arteries and rest are venous exits. Metaphysis and epiphysis are further. Labeling portions of a long bone. A epiphyseal plate made of hyaline cartilage is responsible for long bone growth. The epiphyseal plate has a zonal arrangement, with cartilaginous proliferation occurring closer to the epiphysis, and ossification. It is composed of compact or cortical bone on the outside and the epiphyseal plate, a hyaline cartilage disk in the wider portion of a long bone, called metaphysis, is situated between the growth site and. The central cavity in a long bone where bone marrow is found. The epiphysis is covered by articular cartilage. Within the long bones, the epiphysis is the first to undergo conversion followed by the diaphysis before extending to the metadiaphysis 5,6. Long bones are one of the five bone types that are classified by shape. Long bones consist of a diaphysis, metaphysis and epiphysis. Compact bone forms the outer tissue of bone.
A epiphyseal plate made of hyaline cartilage is responsible for long bone growth. The epiphysis is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone(s). The labels include proximal epiphysis, proximal metaphysis, diaphysis (bone shaft), distal. Compact bone and spongy bone both perform different functions.
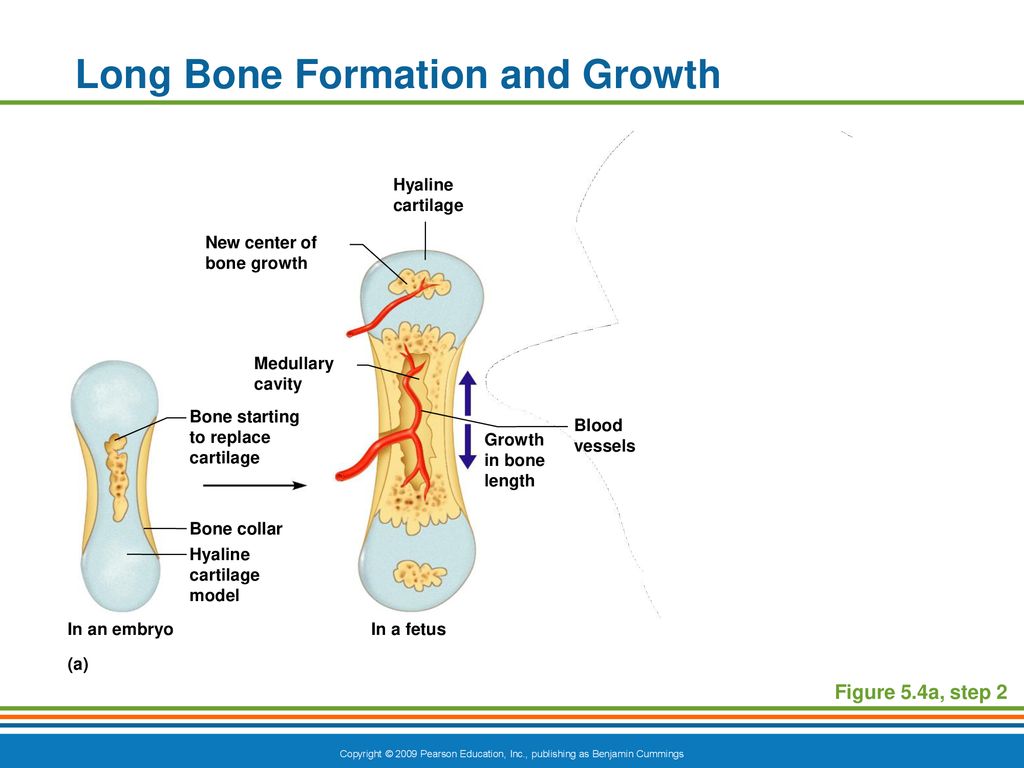
These chondrocytes do not participate in bone growth;
Long bones are one of the five bone types that are classified by shape. The growth plate is located just below the epiphysis and is the portion of the bone in which cartilage proliferates and is mineralized. Vascular supply of long bones depends on several points of inflow, which feed complex sinusoidal networks within the bone. Within the long bones, the epiphysis is the first to undergo conversion followed by the diaphysis before extending to the metadiaphysis 5,6. The metaphysis is the wide portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the narrow diaphysis. They have a shaft part that connects the two ends referred to as epiphysis (mostly spongy bone with a thin layer of compact bone). Note that growth plates do not have to be a linear straight line like in the epiphyseal plate they can be round within the. Distal epiphysis proximal epiphysis diaphysis metaphysis reset. Instead, they secure the epiphyseal plate to the osseous tissue of the epiphysis. Is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. Structure of a long bone, with epiphysis labeled at top.
Long bones include the humerus (upper arm), radius (forearm), ulna (forearm) this image represents the parts of a long bone. The epiphysis is covered by articular cartilage. The newly forming spongy bone (below the growth plate) is not clearly organized as the older spongy bone in the epiphysis above the growth plate. These chondrocytes do not participate in bone growth; The labels include proximal epiphysis, proximal metaphysis, diaphysis (bone shaft), distal. The epiphyseal plate has a zonal arrangement, with cartilaginous proliferation occurring closer to the epiphysis, and ossification.

The growth plate is located just below the epiphysis and is the portion of the bone in which cartilage proliferates and is mineralized.
Label the regions of a long bone. Metaphysis and epiphysis are further detailed in subparts including the cross section and internal anatomy and histology including vascular flow. A epiphyseal plate made of hyaline cartilage is responsible for long bone growth. The epiphyseal plate has a zonal arrangement, with cartilaginous proliferation occurring closer to the epiphysis, and ossification. Is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. Long bones have epiphyseal plate, also known by. Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate (growth. Long bones have epiphyseal plate, also known by physis or growth plate. Anatomy exam 1 at the ohio state university. show full abstract is rarely reported. Anatomy part i at pope john xxiii high school. Distal epiphysis proximal epiphysis diaphysis metaphysis reset. The epiphysis is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone(s). (a) growing long bone showing. The labels include proximal epiphysis, proximal metaphysis, diaphysis (bone shaft), distal.
The outer layer of the bone long bone labeled. Long bones have epiphyseal plate, also known by.
Posting Komentar untuk "Long Bone Labeled Epiphysis"